- High resolution copy number changes (CNVs)
Constitutional Diagnostic Testing
Who are these tests for? This testing category is primarily for patients who already show symptoms of a disorder. Patients without symptoms can also be tested but require different analysis and reporting, please see the “Carrier Individual” or “Carrier Couple” links above for more information.
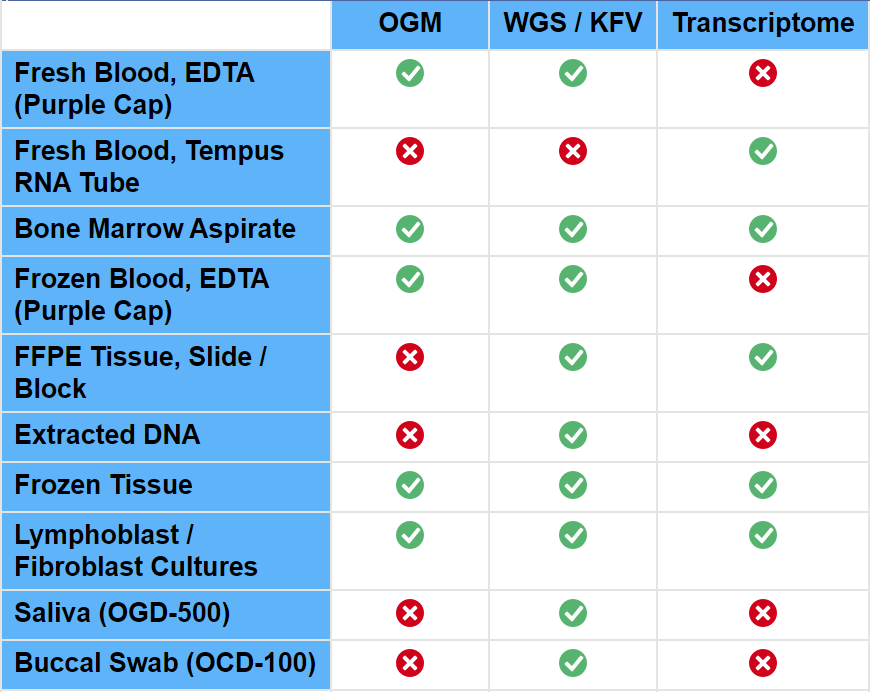
Sample Types: With rare exceptions, in constitutional disorders all cells in the patient's body carry the same disease causing DNA variant(s). This is the reason that these disorders can be diagnosed from different sample types such as blood, saliva, buccal swab, tissue biopsies from any organ or cultured cells. OGM testing requires fresh blood or tissue biopsy.
Why Praxis Genomics? To diagnose the patient's problem, we identify all types of variants over the entire genome of an individual. These include nuclear and mitochondrial single nucleotide polymorphisms and small insertions-deletions, repeat expansions (Fragile X syndrome), contractions (FSHD), and structural variants of all size and type including those that do not result in loss or gain of genetic material such as inversions and translocations.
The Praxis Genomics Technology: We can identify all types of variants because we use Short Read Whole Genome Sequencing (SRG) and Optical Genome Mapping (OGM) together. The complementary strength of the two methodologies, and the fact that the two datasets are analyzed together by the same medical director, results in sensitivity and accuracy that other laboratories cannot match.
The importance of functional testing: Variants identified by SRG and OGM often have not been previously described and it is important to show that they indeed cause the patient's symptoms. Transcriptome (SRT) analysis provides such information based on the quantity and quality of the transcripts made from the affected genes.
Easy to read reports: All this information is filtered and interpreted by a medical doctor. An easy-to-understand, concise report is issued with a clear diagnosis, allowing prognostication and choosing the best possible therapy for the patient.
Financial considerations: Although we recommend that (SRG) and (OGM) tests be performed simultaneously they can also be performed individually or sequentially. We also offer a graded reporting scheme consisting of a Basic Exome, Expanded Exome and Whole Genome analysis from the same genomic dataset at a reduced cost. If the cause of the patient's condition cannot be established based on currently available information, we provide reanalysis of the data one year after the testing was done.
Aneuploidy Testing
Purpose: This test aims to confirm the results of NIPT testing based on WGS information. It is limited to reporting out CNVs greater than 10kb in length. The test is performed in both pre- and post-natal samples. The results can be used to guide reproductive decisions.
Available Tests:
SRG801 - Aneuploidy Testing
Basic Exome
Purpose: This test aims to establish the molecular cause of genetic disorders that people could transfer to their children. The results can be used to guide therapy and prognostication of disease outcomes. This test is for people who already show symptoms of a disorder. We offer carrier testing for people who worry about having variants that would cause them develop disease later in life. The reason for this distinction is that diagnostic and carrier testing data requires different types of analysis and reporting.
Available Tests:
SRG501 - Basic Exome, Proband
SRG502 - Basic Exome, Duo
SRG503 - Basic Exome, Trio
SRG504 - Basic Exome, 4 Sample
SRG505 - Expanded Exome Upgrade per Sample
SRG506 - Basic Genome Upgrade per Sample
Expanded Exome
This test can be upgraded to Whole Genome Sequencing (SRG511) and Optical Genome Mapping (OGM001-004) without providing additional patient sample.
The Expanded Exome -> Whole Genome upgrade architecture protects the customer financially since the upgrade from a negative exome to Expanded Exome or genome costs only the difference between the price of the respective tests and no new sample is required.
Available Tests:
SRG507 - Expanded Exome, Proband Only
SRG508 - Expanded Exome, Duo
SRG509 - Expanded Exome, Trio
SRG510 - Expanded Exome, 4 Sample
SRG511 - Whole Genome Upgrade per Sample
Whole Genome Sequencing
PLA Code: 0265U
Purpose: This test aims to establish the molecular cause of genetic disorders that people could transfer to their children. The results can be used to guide therapy and prognostication of disease outcomes. This test is for people who already show symptoms of a disorder. We offer carrier testing for people who worry about having variants that would cause them develop disease later in life. The reason for this distinction is that diagnostic and carrier testing data requires different types of analysis and reporting.
Available Tests:
SRG001 - Whole Genome Sequencing, Proband
SRG002 - Whole Genome Sequencing, Duo
SRG003 - Whole Genome Sequencing, Trio
SRG004 - Whole Genome Sequencing, 4 Sample
Optical Genome Mapping
PLA Code: 0264U
Purpose: Optical Genome Mapping, (OGM) is for the evaluation of large-scale changes in the DNA that can cause heritable disorders of any kind. Changes that are detected by OGM are the following:
- Intra- and inter- chromosomal translocations both balanced and unbalanced
- Inversions
- Complex chromosomal rearrangements
- Contraction of a subtelomeric macrosatellite repeats (e.g. D4Z4 FSHD)
- Tandem repeat expansions (Fragile X, Myotonic Dystrophy 1 and 2, C9ORF72, and others)
Available Tests:
OGM001 - Optical Genome Mapping Proband
OGM002 - Optical Genome Mapping Duo
OGM003 - Optical Genome Mapping Trio
OGM004 - Optical Genome Mapping 4 Sample
Whole Genome Sequencing (Long Read)
Purpose: This test aims to establish the molecular cause of genetic disorders that people could transfer to their children. The results can be used to guide therapy and prognostication of disease outcomes. This test is for people who already show symptoms of a disorder. We offer carrier testing for people who worry about having variants that would cause them develop disease later in life. The reason for this distinction is that diagnostic and carrier testing data requires different types of analysis and reporting.
Available Tests:
LRS001 - Long Read Sequencing
Whole Genome Methylome Testing (Long Read)
Purpose: This test aims to establish the molecular cause of imprinting genetic disorders, such as Prader-Willi/Angelman Syndromes, Beckwith-Wiedemann/Silver-Russell Syndromes. Also this test allows determination of biased X chromosome inactivation. The results can be used to guide therapy and prognostication of disease outcomes. This test is for people who already show symptoms of a disorder.
Available Tests:
LRS101 - Long Read Methylome
Transcriptome
PLA Code: 0266U
Purpose: Transcriptome analysis is a method that allows evaluation of the functional consequences of DNA variants discovered by optical genome mapping or DNA sequencing. These are:
- Deletions, insertions, inversions, translocations affecting
- regulatory regions resulting in altered gene expression or alternative transcription initiation and termination sites
- coding regions resulting in shortened or expanded or chimeric transcripts
- imprinted loci resulting in some cases complete loss of transcription (Prader Willi sy.)
- Single nucleotide changes or small insertions deletions affecting
- splicing resulting in exon skipping or alternative splicing
- translation initiation and termination resulting in truncated or absent transcripts
- Repeat number changes affecting
- chromatin structure and adjacent gene expression (FSHD)
- Repeat expansions affecting transcript levels & splicing.
Available Tests:
SRT401 - Transcriptome Proband
SRT402 - Transcriptome Duo
SRT403 - Transcriptome Trio
SRT404 - Transcriptome 4 Sample
Combination Testing
PLA Code: 0267U
Purpose: This test combines Optical Genome Mapping (OGM) and Whole Genome Sequencing (SRG) with potential addition of transcriptome (SRT) sequencing. It aims to establish the molecular cause of genetic disorders that people could transfer to their children. The results can be used to guide therapy and prognostication of disease outcomes. This test is for people who already show symptoms of a disorder. We offer carrier testing for people who worry about having variants that would cause them develop disease later in life. The reason for this distinction is that diagnostic and carrier testing data requires different types of analysis and reporting.
Available Tests:
PRX001 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping and Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis, Proband
PRX002 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping and Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis, Duo
PRX003 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping and Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis, Trio
PRX004 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping and Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis, 4 Sample
PRX007 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping, Whole Genome Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis, Proband
PRX008 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping, Whole Genome Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis, Duo
PRX009 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping, Whole Genome Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis, Trio
PRX010 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping, Whole Genome Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis, 4 Sample
PRX101 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping and External Data Analysis, Proband
PRX102 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping and External Data Analysis, Duo
PRX103 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping and External Data Analysis, Trio
PRX104 - Combined Optical Genome Mapping and External Data Analysis, 4 Sample
FSHD Testing
Purpose: This test is to diagnose FSHD. Optical genome mapping can determine whether the patient has FSHD1 and whole genome sequencing can diagnose FSHD2. At Praxis Genomics, we offer testing for FSHD1 and FSHD2 individually, as well as in combination.
Available Tests:
OGM201 - FSHD1 Proband
OGM202 - FSHD1 Due
OGM203 - FSHD1 Trio
OGM204 - FSHD1 4 Sample
SRG201 - FSHD2 Testing Proband
SRG202 - FSHD2 Testing Duo
SRG203 - FSHD2 Testing Trio
SRG204 - FSHD2 Testing 4 Sample
PRX201 - FSHD1 and 2 Testing, Proband
PRX202 - FSHD1 and 2 Testing, Duo
PRX203 - FSHD1 and 2 Testing, Trio
PRX204 - FSHD1 and 2 Testing, 4 Sample
Repeat Expansion Sizing
Purpose: Repeat expansions can be identified using Whole Genome Sequencing, but their size cannot be precisely determined. We offer this test based on optical genome mapping to accurately size repeat expansions greater than 500bp in length.
Available Tests:
OGM101 - Repeat Sizing Proband
OGM102 - Repeat Sizing Duo
OGM103 - Repeat Sizing Trio
OGM104 - Repeat Sizing 4 Sample
Known Familial Variant Testing
Available Tests:
KFV001 - Targeted assessment for 1 variant in one person
© Praxis Genomics, LLC 2020